
calculating the #weightedmean is actually pretty easy if you know what to do.
#Weighted standard deviation formula stats how to#
do you ever wonder how your grade is calculated when there are weights applied to each category? watch and find out how how to find weighted mean in statistics|weighted mean in statistics|weighted mean example. remember that each data point is multiplied by a given weight, in this video we discuss how to find, or calculate the weighted mean, average or score of a data set, grades, or test scores in computing for weighted mean, sample data, ms excel, table interpretation. here is a list of topics: 0:00 how to this video covers how to find the weighted mean for a set of data. This statistics video tutorial explains how to find the weighted mean and weighted average. How To Find The Weighted Mean And Weighted Average In Statistics otherwise, multiply each weight w by its matching value x, sum that all up, and divide by the sum of weights: weighted mean = Σwx Σw. when the weights add to 1: just multiply each weight by the matching value and sum it all up. Weighted mean: a mean where some values contribute more than others. the weighted average of the time you spent working out for the month is 20.9 minutes. example: sum of variables (weight) sum of all weights = weighted average. The formula for finding the weighted average is the sum of all the variables multiplied by their weight, then divided by the sum of the weights.
#Weighted standard deviation formula stats free#
a free online tool called the weighted mean calculator is used to calculate the weighted mean for the given range of values. when all the weights are equal, then the weighted mean is similar to the arithmetic mean.

Weighted mean is defined as an average computed by giving different weights to some of the individual values. in such an example, the student would multiply the weighing of all assessment items in the course (e.g., assignments, exams, projects, etc.) by the respective grade that was obtained in each of the categories. For example, a student may use a weighted mean in order to calculate his her percentage grade in a course. You should perhaps use a Bayesian estimate or Wilson score interval.Weighted mean formula can be applied to calculate the average returns from a portfolio comprising of different financial instruments financial instruments financial instruments are certain contracts or documents that act as financial assets such as debentures and bonds, receivables, cash deposits, bank balances, swaps, cap, futures, shares. Weighting by the inverse of the SEM is a common and sometimes optimal thing to do. Taking percentages the way you are is going to make analysis tricky even if they're generated by a Bernoulli process, because if you get a score of 20 and 0, you have infinite percentage. You don't have an estimate for the weights, which I'm assuming you want to take to be proportional to reliability.

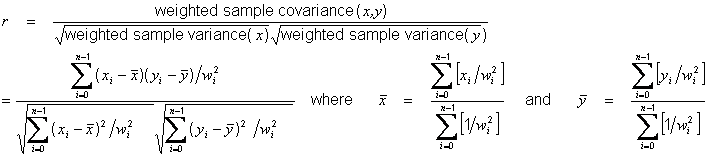
Where $x^* = \sum w_i x_i / \sum w_i$ is the weighted mean. In any case, the formula for variance (from which you calculate standard deviation in the normal way) with "reliability" weights is (Actually, all of this is rubbish-you really need to use a more sophisticated model of the process that is generating these numbers! You apparently do not have something that spits out Normally-distributed numbers, so characterizing the system with the standard deviation is not the right thing to do.) Instead, you need to use the last method.

You generate your data from frequencies, but it's not a simple matter of having 45 records of 3 and 15 records of 4 in your data set. In your case, it superficially looks like the weights are frequencies but they're not. you are just trying to avoid adding up your whole sum), if the weights are in fact the variance of each measurement, or if they're just some external values you impose on your data. In particular, you will get different answers if the weights are frequencies (i.e. The key is to notice that it depends on what the weights mean. The formulae are available various places, including Wikipedia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
